OAS EXPLAINS: IDENTITY - DRIVEN SECURITY FOR THE MODERN ENTERPRISE

Mantra for Cyber Criminals – “It is easier to Login than to Hack!"
An Identity-Driven Cyber Attack is a type of cyber threat where attackers target and exploit digital identities (such as usernames, passwords, API keys, tokens, or privileged accounts) rather than trying to directly break through firewalls or exploit technical vulnerabilities.
Since modern enterprises rely heavily on identity for access control (especially in cloud and remote work environments), compromising an identity often gives attackers the same level of access as a legitimate user—making detection harder and impact greater.
Key Characteristics of Identity-Driven Attacks
- Credential Theft – Stealing login credentials through phishing, malware, or credential dumps.
- Privilege Escalation – Once inside, attackers elevate their access by exploiting misconfigured permissions or compromised admin accounts.
- Account Takeover (ATO) – Hijacking user or service accounts to impersonate legitimate activity.
- Pass-the-Hash / Pass-the-Ticket – Using authentication tokens or hashes to bypass password entry.
- Abuse of Non-Human Identities – Exploiting API keys, machine identities, or service accounts that often have broad access.
- Living-off-the-Land Techniques – Attackers use legitimate credentials and tools, making their actions blend in with normal activity.
Examples
- A phishing email tricks an employee into entering credentials into a fake login page → attacker uses them to log into Office 365 or cloud apps.
- An attacker exploits weak MFA policies and gains access to an executive’s account → uses it to move laterally across systems.
- A compromised API key from a developer’s repository gives attackers direct access to cloud storage or databases.
Why They’re Dangerous
- Harder to Detect – Attack traffic often looks like normal user activity.
- High Impact – Compromised admin or service accounts can give attackers full control over critical systems.
- Bypasses Traditional Defenses – Firewalls and antivirus won’t block a “legitimate” login.
How to combat Identity - Driven attacks
Identity-Driven Security is a modern cybersecurity approach that places user and machine identities at the center of access control and threat protection. Instead of relying solely on traditional perimeter defenses (like firewalls or VPNs), it secures digital environments by continuously verifying who (or what) is requesting access, under what conditions, and with what level of trust.
This model is essential for enterprises operating in hybrid, cloud, and remote-first environments where users, applications, and devices often operate outside traditional corporate networks.
Core Principles of Identity-Driven Security
- Zero Trust Mindset – Never trust, always verify. Every request for access is validated regardless of location or network.
- Continuous Authentication – Beyond simple login, identity is revalidated during sessions based on behavior, device health, and risk signals.
- Context-Aware Access – Access decisions consider multiple factors: user role, device compliance, geolocation, and real-time risk.
- Least Privilege Enforcement – Users and applications only get the access required to perform their tasks—nothing more.
- Integration of Identity & Security – Identity services (e.g., SSO, MFA, directory services) are tightly linked with security policies and monitoring.
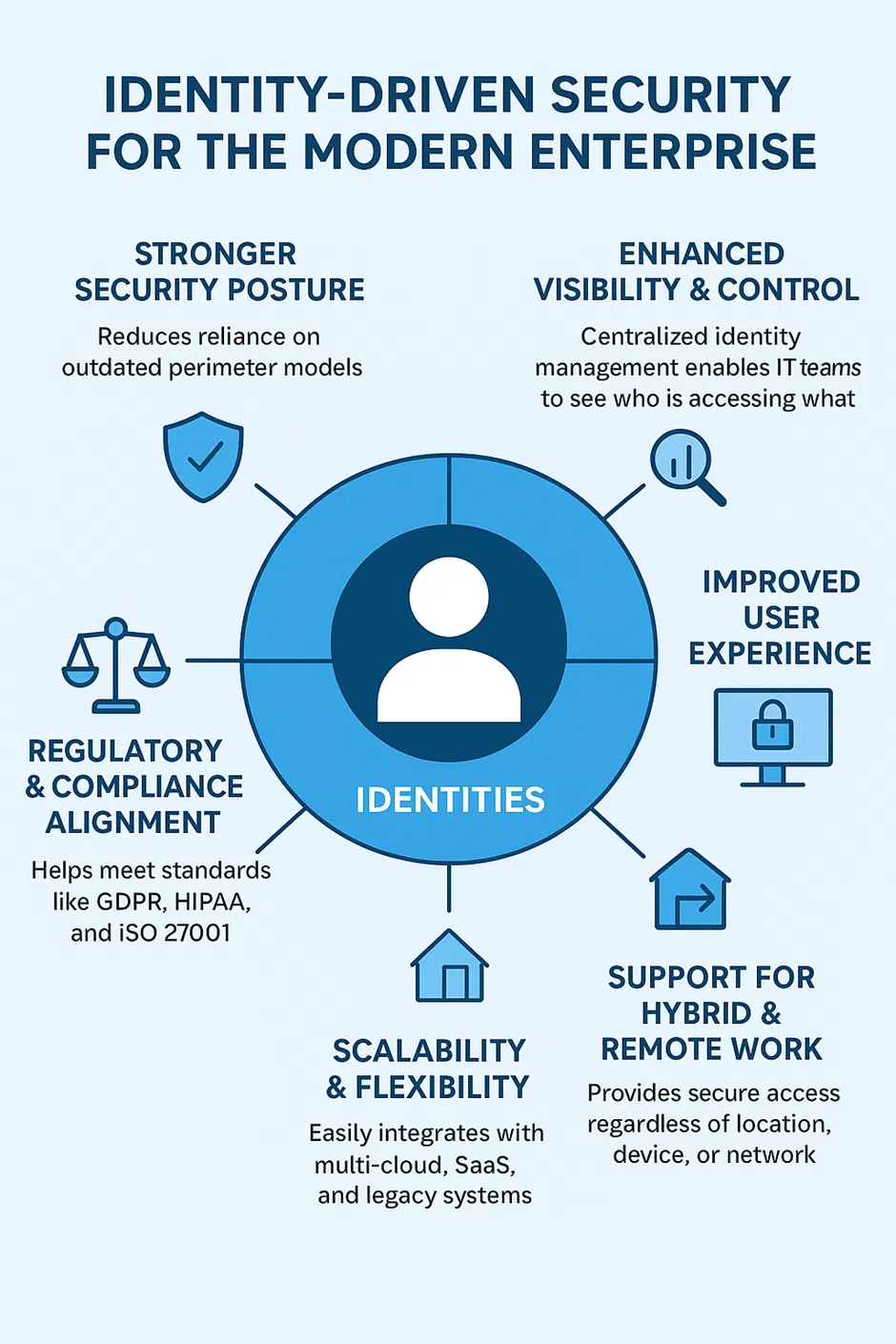
Benefits for the Modern Enterprise
Stronger Security Posture
- Reduces reliance on outdated perimeter models.
- Protects against credential theft, insider threats, and phishing attacks by requiring multi-factor and adaptive authentication.
Enhanced Visibility & Control
- Centralized identity management enables IT teams to see who is accessing what across cloud, SaaS, and on-premises resources.
Improved User Experience
- Single Sign-On (SSO) and password-less authentication simplify access while maintaining security.
- Adaptive policies reduce unnecessary friction (e.g., only prompt MFA when risk is high).
Support for Hybrid & Remote Work
- Provides secure access regardless of location, device, or network.
- Ensures consistent policies across distributed environments.
Regulatory & Compliance Alignment
- Helps meet standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 by enforcing granular access controls and audit trails.
Scalability & Flexibility
- Easily integrates with multi-cloud, SaaS, and legacy systems.
- Supports dynamic workforces, contractors, and partners with tailored access policies.
In essence: Identity-Driven Security shifts security from where a user is to who they are and how trustworthy their request is. For modern enterprises, it is the cornerstone of Zero Trust security and a prerequisite for enabling secure digital transformation.